PROJECT MANAGEMENT TERMS & DEFINITIONS
Microsoft Project is a project management system, which assist the project managers to execute and control the project activities effectively in order to meet the sponsors needs and expectations from a project.
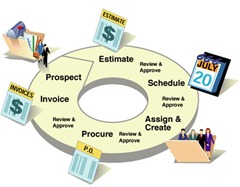
Project management involves the planning, scheduling and controlling of the activities in a project

- Planning – Defining the objectives of the project and listing the tasks.
- Scheduling – Arranging the tasks in the order in which they are to be performed and allocating the resources.
- Controlling – Calculating the optimum, durations of each activity and quantity of resources to bring out the successful completion of the project.
Network planning technique can be used for project management. In this technique large projects are broken down to individual jobs or events and arranged in logical network. Network planning helps in planning, scheduling and controlling, in order to complete the project economically in minimum available time with limited available resources.
The important terms related to project planning are:
Event
An event is a specific instant of time, which makes the start or end of an activity. Event consumes neither time nor resources.
Activity
An activity is the actual performance of the task and requires time and resources for its completion. It is the work required to complete a specific task.
Predecessor activity
The activity proceeding to any given activity is called the predecessor activity.
Successor activity
The activity succeeding to any given activity is called the successor activity.
Duration
Duration is the estimated or actual time required to complete a task or an activity.
Earliest start time (EST)
It is defined as the earliest possible time at which an activity can start. It is calculated by moving from first to last event in a network diagram.
Earliest finish time (EFT)
It is the earliest possible time at which an activity can finish.
EFT = EST + duration of that activity.
Latest finish time (LFT)
It is calculated by moving from last event to the first event of the network diagram.
Latest start time
It is the latest possible time by which an activity can start.
LST = LFT – duration of that activity.
Float or Slack
Stack is with reference to an event and float is with reference to an activity. Float is the difference between time available for completing an activity and the time necessary to complete an activity.
Total Float
It is the time span by which the starting and finishing an activity can be delayed without delaying the completion of the project. It is the additional time, which a non critical activity can consume without increasing the project duration.
Critical path
It is the sequence of critical activities, which decide the total project duration. A critical path consumes maximum resources. It is the longest path and consumes maximum time. It is the one, which connects the events having zero minimum float.
PERT (Project Evaluation and Review Technique)
It is a probabilistic model with uncertainty in activity duration. It is an event oriented approach used for planning, controlling and reviewing the project. The expected time for each activity can be calculated using three time estimates-
- Optimistic time (to)
- Most likely time (tm)
- Pessimistic time (tp)
It is used to find the applications in projects where resources(3m – en, materials and money) are always made available as and when required.
CPM (Critical Path Method)
CPM is a deterministic model with well known activity time based upon past experience. It assumes that , the expected time is actually the time taken. It is an activity oriented system and marks the critical activities. CPM is employed to those projects where minimum overall cost is important and there is better utilization of resources.
Network Updating
It is defined as an adjustment to the network diagram, which becomes necessary owing to departure from the project schedule laid down earlier. It is the process of incorporating the changes in the network, which have occurred due to planning and rescheduling.
Resource
A resource is a physical variable such as labour, finance, equipment and space, which will impose limitation on time for the project.
Resource Smoothing
This implies scheduling the activities within the limit of their total float, such that fluctuations in the resource requirements are minimized. In resource smoothing the main constraint is the project duration time. But the activities having floats are shifted so that a uniform demand on the resources is achieved.
Resource Leveling
In resource leveling, the main constraint would be the resources and if the maximum demand on any resource is not exceed a certain limit, the activities will then have to be rescheduled so that the total demand on the resource at any time will be within the limit. The project duration time consequently is exceeded.
FOUR PHASES OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT
We have learnt what is project management. There are four phases of project management which are required to manage projects efficiently on quality, time and costs.
1. Defining and organizing the project: Defining project is the first step in the project management process. In this process you identify the business need for and objectives of the project; clarify competing demands and watch for scope creep. Organizing projects means defining roles and responsibilities, create a project charter, and develop high-level time and cost estimates. Organizing of the project is an important step towards planning of the project.
2. Planning the project: Planning phase of the project management is done based on organization done in the previous step. In this phase you assemble your team and assign tasks to individuals, develop a budget for the project, develop a schedule and create a communications plan. While doing planning for the project, effective and clear estimate of the time and costs are done. If any changes needs to be done in the planning for more clear estimates of time and costs, sometimes organization of the project is reviewed.
3. Executing the project: In this phase of the project, team is ready to launch the project. Team members monitor and control progress in terms of cost, time, and quality; and manage risk. It is kept in the mind that during the execution of the project, it is required to keep the process monitored for timely completion of the project, as per schedules. If the project work is not carried out as per schedules, and execution is well behind the schedule, then cost and quality of the project will be effected. If the time of the project is increased, it increases the cost of manpower and their allowances affecting the budget set for the project. Meanwhile, if the project is still required to be completed on time, then the quality of the project is effected. Always remember, Quality = Time + Cost. If cost or time is effected, quality of the project is effected.
4. Closing down the project: Once the execution of the project is completed, the project team evaluates the team’s performance, documents related to the project are achieved, lessons learned form the experiences in the project is captured and celebrate the project’s completion.
Role of Project Manager

The responsibility of project manager to make sure that the customer is satisfied and the work scope is completed in a quality manner, using budget, and on time. The Project Manager has primary responsibility for providing leadership in planning, organizing and controlling the work effort to accomplish the project objectives. In other words, the project manager provides the leadership to project team to accomplish the project objective. The project manager coordinates the activities of various team members to ensure that they perform the right tasks at the proper time, as a cohesive group. The different roles of project manager are as follows:
- Planning
- Organizing
- Controlling
- Leading
- Communicating
- Cognitive functions
- Self management functions
- Motivational and personal development functions
- Customer awareness functions
- Organizational savvy functions
Planning
First, the project manager clearly defines the project objectives and reaches agreement with the customer on this objective. The manager then communicate this objective to the project team in such a manner as to create a vision of what will constitute successful accomplishment of the objective. The project manager spearheads development of a plan to achieve the project objectives. By involving the project team in developing this plan, the project manager ensures more comprehensive plan than he or she could develop alone. Furthermore, such participation gains the commitment of the team to achieve the plan. The project manager reviews the plan with the customer to gain endorsement and then sets up the project management information system-either manual or computerized-for comparing actual progress to plan progress. It’s important that this system be explained to the project team so that the team can use it properly to manage the project.
Organizing
Organizing involves securing the appropriate resources to perform the work. First, the project must decide which tasks should be done in-house and which tasks should be done by subcontractors or consultants. For tasks that will be carried out in-house, the project manager gains a commitment from the specific people who will work on the project. For tasks that will be performed by subcontractors, the project manager clearly defines the work scope and deliverables and negotiates a contract with each subcontractor. The project manager also assigns responsibility and delegates’ authority to specific individuals or subcontractors for the various tasks, with the understanding that they will be accountable for the accomplishment of their tasks within the assigned budget and schedule. For large projects involving many individuals, the project manager may designate leaders for specific group of tasks. Finally, and most important, the task of organizing involves creating an environment in which the individuals are highly motivated to work together as a project team.
Controlling
To control the project, the project manager implements a management information system designed to track actual progress and compare it with planned progress. Such a system helps the manager distinguish between busy-ness and accomplishments. Project team members monitor the progress of their assigned tasks and regularly provide data on progress, schedule and cost. These data are supplemented by regular project review meetings. If actual progress falls behind planned progress or unexpected events occur the project manager takes immediate action. He or she obtains input and advice from team members regarding appropriate corrective actions and how to replan those parts of the project. It’s important that problems and even potential problems, be identified early and action taken. The project manager cannot take a “let’s wait and see how things works out” approach- things never works out on their own. He or she must intervene and be proactive, resolving problems before they become worse.
Leading
Project manager fosters development of a common mission and vision to the team members. He should clearly define roles, responsibilities and performance expectations for all his team members. He uses leadership style appropriately to situation or stage of team development. He should be able to foster collaboration among team members. He should provide clear direction and priorities to his team members. He should be efficient enough to remove obstacles that hamper team progress, readiness or effectiveness. He should promote team participation in problem solving and decision making as appropriate. He should pass credit on to team, and promotes their positive visibility to upper management. He should appreciate, promote and leverage the diversity within the team.
Communicating
The Project Manager should be able to communicate effectively with all levels inside and outside of the organizations. He should be able to negotiate fairly and effectively with the customers/subcontractors. He should be able to bring conflicts into the open and manages it collaboratively and productively with the help of other team members. He should be able to able to influence without relying on coercive power or threats. He should be able to convey ideas and information clearly and concisely, both in writing and orally to all the team members.
Cognitive functions
The project manager should identify the problem and gathers information systematically and seeks input from several sources. He should then consider a broad range of issues or factors while solving these problems. For this he collects the appropriate quantity of data for the situation and discusses it with all the team members before making a decision. He then draws accurate conclusions from quantitative data and makes decisions in an unbiased, objective manner using an appropriate process. For this process of decision making he understands the concept of risk versus return and makes decision accordingly.
Self management functions
The project manager should be able to maintain focus and control when faced with ambiguity and uncertainty and should be able to show consistency among principles, values and behavior. He should be resilient and tenacious in the face of pressure, opposition, constraints, or adversity. Being the head of the project he should manage implementations effectively and should recognize as someone “who gets things done.” He should continuously seek feedbacks from the team members and modify his behavior accordingly. He should take keen interest in learning and self development opportunities.
Motivational and personal development functions
Project manager should consider individual skills, values and interest of all his team members when assigning or delegating tasks to them. He should allow team members an appropriate amount of freedom to do the job. He should accurately access individual strength and development needs of his team members to complete the work effectively. He should continuously offer opportunities for personal and professional growth to his team members. He should arrange for training program and continuously seeks support to his team member when needed. He should pass credit on to the individuals and promote their positive visibility to upper management. He should give timely, specific and constructive feedback to all his team members.
Customer awareness functions
Project manager should be able to anticipate customer’s needs effectively and proactively strives to satisfy them. He should be able to accurately translate the customer’s verbalized wants into what they actually needs. He should be able to understand customers and their business and actively build and maintain strong customer relationships. He should understand customer’s issues, concerns and queries and try to resolve them effectively. He should actively strive to exceed customer expectations.
Organizational savvy functions
Project manager should involve the right people at the right time for a particular job. Understands, accepts and properly uses power and influence in relationships. He should build and leverage formal and informal networks to get things done. He should know the mission, structure and functions of the organizations and others. He should understand profitability and general management philosophy. He balances interests and needs of team/project with those of the broader organization.
No comments:
Post a Comment